Frequent droughts in sub-Saharan Africa imply water stress for rainfed agriculture
and, ultimately, food insecurity, underlining the region’s vulnerability to climate
change. Yet, in the maize-growing areas, farmers have been given new droughtcoping
options following the release and availability of drought-tolerant maize
varieties (DTMVs).
These varieties are being disseminated through the National Agricultural Research and Extension Systems in collaboration with seed companies; however, their adoption still appears somewhat modest, and empirical studies on their adoption potential and associated drivers are scarce.
We use empirical data from Uganda to estimate the actual and potential adoption rates and the adoption determinants of DTMVs under information and seed access constraints.
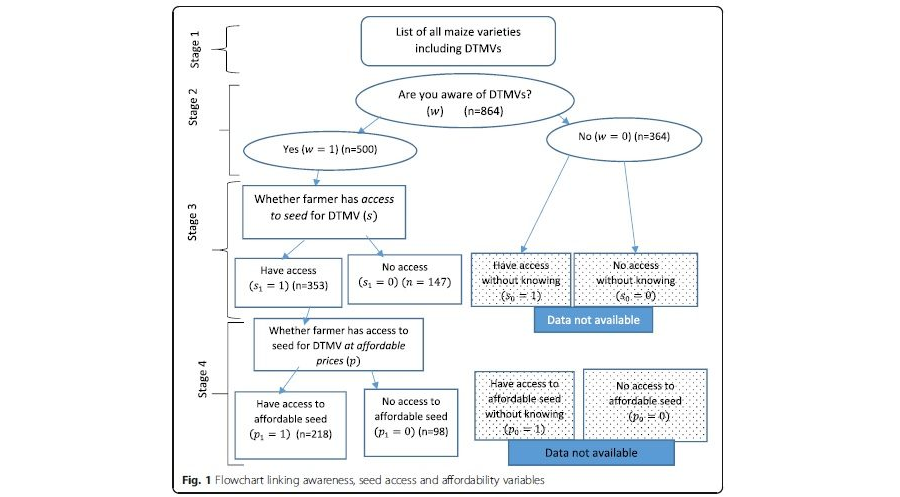
Adoption rates for DTMVs could have been up to 22% in 2015 instead of the observed sample
adoption rate of 14% if the whole population had been exposed to them. The adoption rate could increase to 30% if seed were availed to the farming population and to 47% if seed were sold at a more affordable price to farmers.
The observed adoption rate of 14% implies gaps in the potential adoption rates of 8%, 16%, and 33% because of a lack of awareness, a lack of seed access, and high seed prices, respectively.
The findings underscore the role of both market and non-market-based
approaches and the potential to further scale the cultivation of DTMVs in Uganda.